Software
Some projects that are publicly avaiable are listed here. More can be found on my GitHub page.
torch-harmonics
torch-harmonics is a differentiable implementation of the Spherical Harmonic transform in PyTorch. It was originally implemented to enable Spherical Fourier Neural Operators (SFNO). It uses quadrature rules to compute the projection onto the associated Legendre polynomials and FFTs for the projection onto the harmonic basis. This algorithm tends to outperform others with better asymptotic scaling for most practical purposes.
torch-harmonics uses PyTorch primitives to implement these operations, making it fully differentiable. Moreover, the quadrature can be distributed onto multiple ranks making it spatially distributed.
torch-harmonics has been used to implement a variety of differentiable PDE solvers which generated the animations below. Moreover, it has enabled the development of Spherical Fourier Neural Operators (SFNOs)
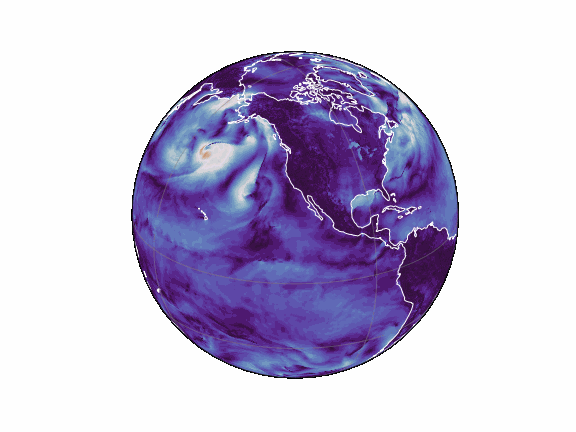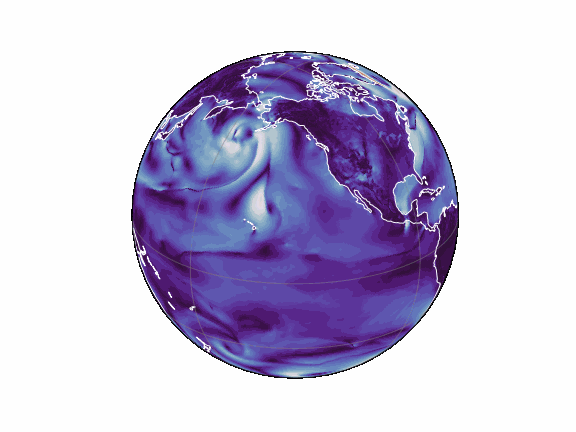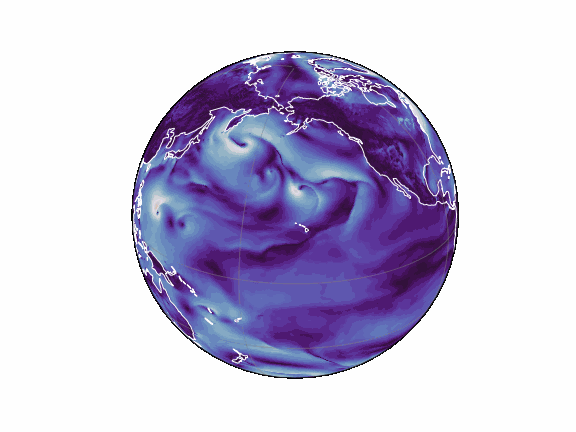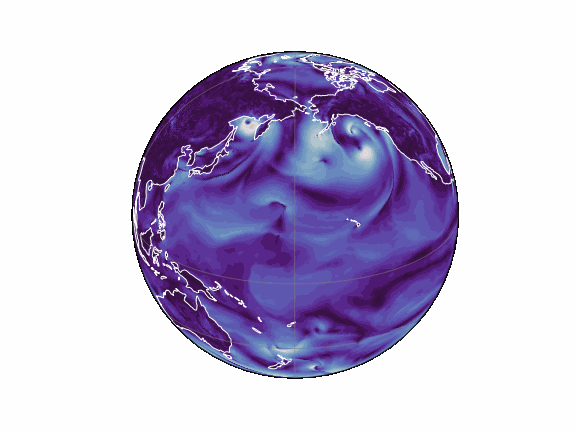
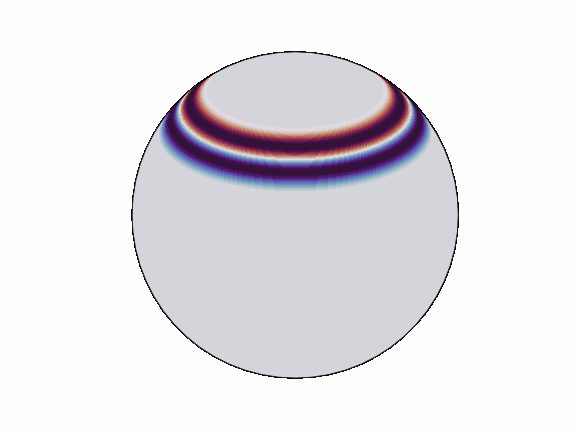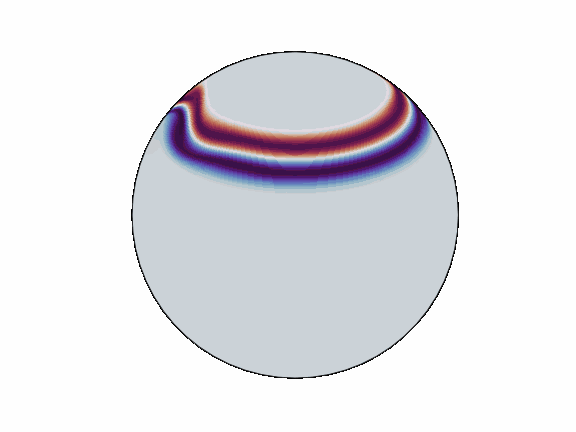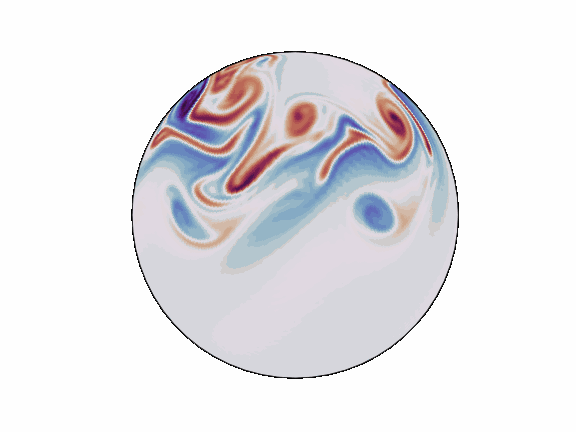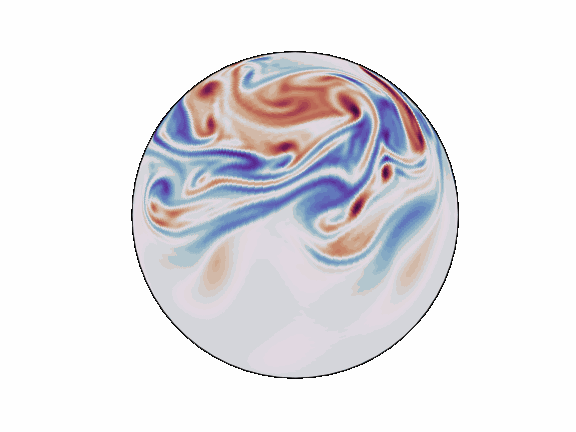
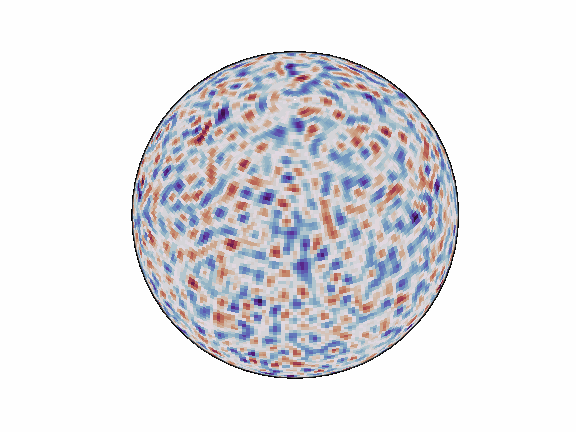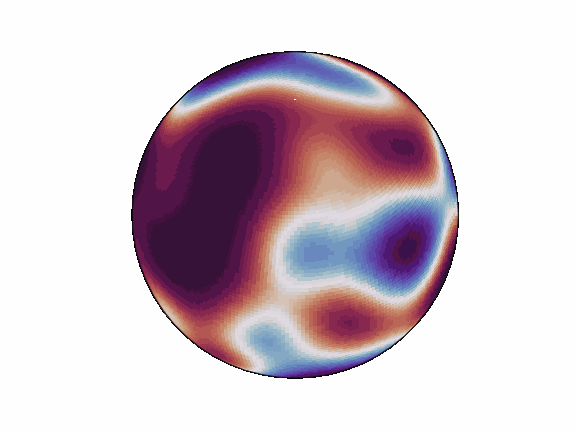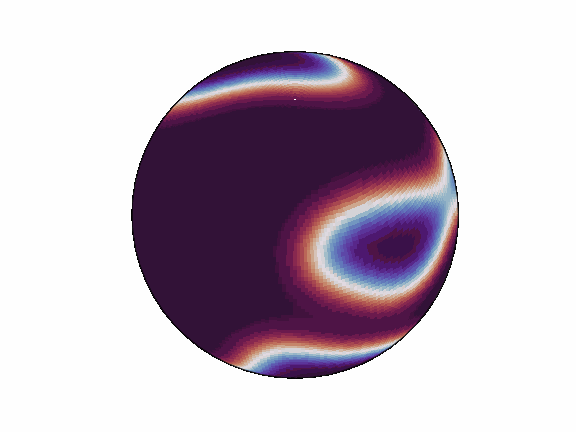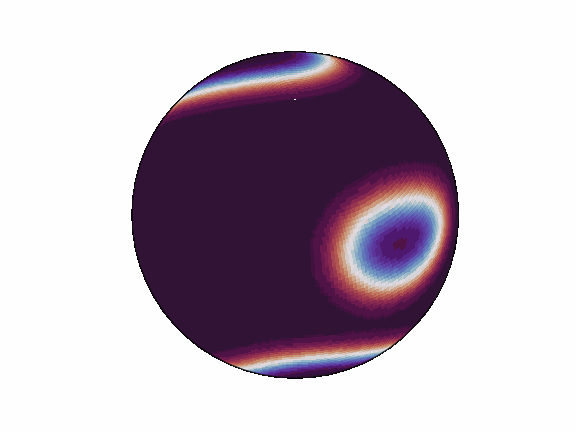
pip install torch-harmonics
Build in your environment using the Python package:
git clone git@github.com:NVIDIA/torch-harmonics.git
cd torch-harmonics
pip install -e .
makani
Makani (the Hawaiian word for wind 🍃🌺) is an experimental library designed to enable the research and development of machine-learning based weather and climate models in PyTorch.
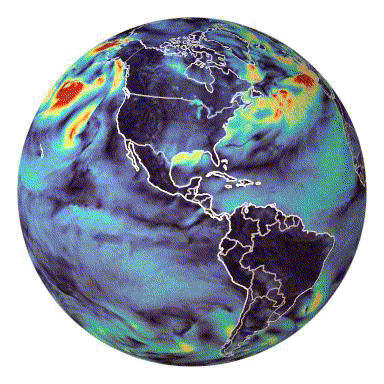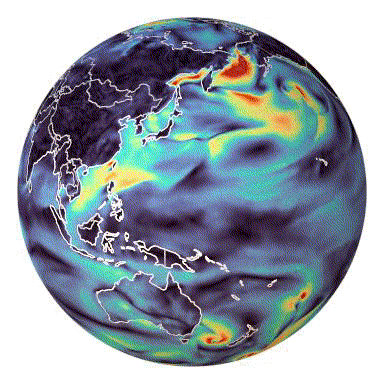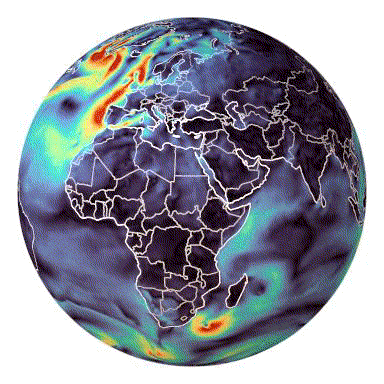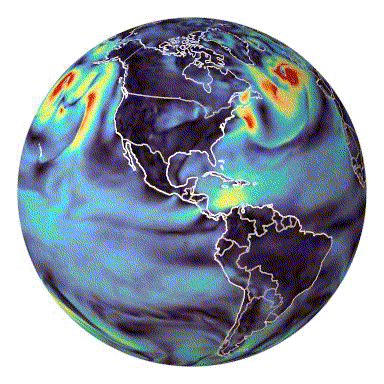
Makani was started by engineers and researchers at NVIDIA and NERSC to train FourCastNet, a deep-learning based weather prediction model.
Makani is a research code built for massively parallel training of weather and climate prediction models on 100+ GPUs and to enable the development of the next generation of weather and climate models. Among others, Makani was used to train Spherical Fourier Neural Operators (SFNO) and Adaptive Fourier Neural Operators (AFNO) on the ERA5 dataset. Makani is written in PyTorch and supports various forms of model- and data-parallelism, asynchronous loading of data, unpredicted channels, autoregressive training and much more.
HssMatrices.jl
HssMatrices is a Julia package for hierarchically semi-separable (HSS) matrices. These matrices are a type of hierarchically structured matrices, that arise in the context of solving PDEs numerically, among others. HssMatrices.jl is intendend to help users experiment with HSS matrices and related algorithms. HssMatrices.jl implements compression routines, HSS arithmetic, as well as helpful routines for clustering and visualization. These matrices have structures similar to the one in the illustration below.
You can install HssMatrices with the built in package manager by running
(@v1.6) pkg> add HssMatrices
HierarchicalSolvers.jl
Hierarchical solvers is an approximate sparse direct solver, entirely written in Julia. It can run in superlinear complexity as approximate solver employing lowrank and hierarchically structured low-rank (HSS) matrices to compress Gauss transforms and Schur complements. As such it can be utilzed as a preconditioner.
Extensions to nodal-dg
nodal-dg is a Matlab library for nodal discontinuous Galerkin methods, originally written by Jan S. Hesthaven and Tim Warburton. nodal-dg-extensions exteds its capabilities to continuous Galerkin methods. It makes heavy use of the original discontinuous Galerkin datastructures for triangular meshes and extends them by adding a mapping which keeps track of duplicated points, which in the continuous Galerkin framework have to be mapped onto a single point. The resulting library is useful for research and development settings, especially if switching between discontinuous and continuous Galerkin methods is necessary, or, if arbitrary order continuous Galerkin methods are of interest. The illustration below shows the solution to a Helmholtz problem computed using the continuous Galerkin method. 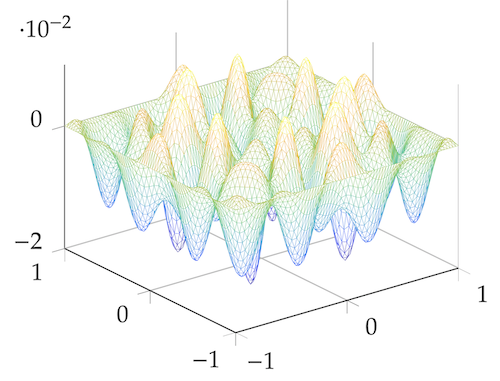
As of now, the extension includes the following features:
- High-order continuous Galerkin (CG/FEM) method on triangular meshes using the nodal-dg datastructures
- DG method for the high-contrast Poisson problem
- IPDG method for linear elasticity in 2D
- Routines for generating a nested dissection for the structured elimination of the resulting matrices
- Plotting routines designed to visualize the results
- Test routines designed to check behaviour under h- and p-refinement


